Decoding the Dow: A Relaxed Guide to the Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), often simply called “the Dow,” is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 30 large, publicly owned companies trading on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq. It’s one of the oldest and most widely followed stock market indices in the world.
Why is the Dow Important?
Think of the Dow as a snapshot of the overall health of the U.S. economy. It’s like a giant thermometer that measures how well these 30 major companies are doing.
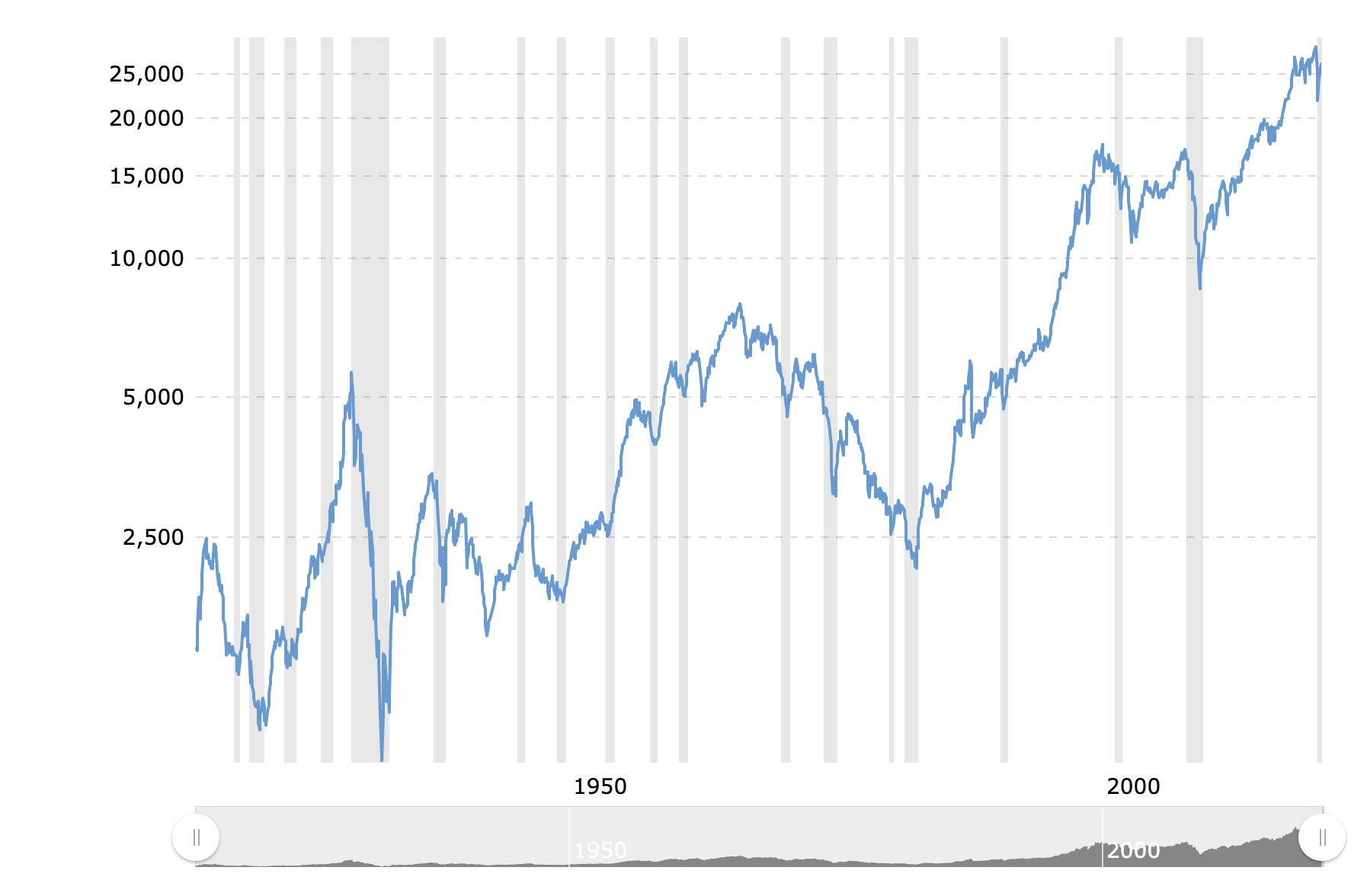
Market Sentiment: The Dow reflects investor sentiment. When the Dow is rising, it generally indicates that investors are optimistic about the economy and believe that company profits will increase. Conversely, a falling Dow suggests that investors are worried about the economy and expect lower profits.
Understanding the Dow: A Simple Analogy
Imagine you have 30 friends, each representing one of the 30 companies in the Dow. Every day, you track how much money each friend makes. The Dow is like calculating the average income of these 30 friends. If most of your friends are making more money, the average income (the Dow) will go up. If many of your friends are making less money, the average income will go down.
How Does the Dow Actually Work?
The Dow is a price-weighted index. This means that companies with higher stock prices have a greater influence on the overall index value.
Price-Weighted: Imagine you’re calculating the average price of 30 different items. A $10,000 car will have a much bigger impact on the average price than a $10 ice cream cone. Similarly, companies with higher stock prices have a greater weight in determining the Dow’s value.
Key Components of the Dow:
The Dow includes 30 large, well-known companies across various sectors of the economy, such as:
Technology: Microsoft, Apple, Intel
Factors That Influence the Dow:
Numerous factors can cause the Dow to fluctuate:
Economic Growth
Strong economic growth: When the economy is expanding, businesses tend to perform better, leading to higher stock prices and a rising Dow.
Interest Rates
Rising interest rates: Higher interest rates can increase borrowing costs for businesses, potentially slowing down economic growth and impacting corporate profits.
Consumer Confidence
High consumer confidence: When consumers feel optimistic about the economy, they tend to spend more money, which benefits businesses and boosts stock prices.
Global Events
Political uncertainty: Geopolitical events, such as wars, trade disputes, and political instability, can create uncertainty in the markets and cause the Dow to decline.
Company Performance
Strong earnings reports: When companies report strong earnings and revenue growth, their stock prices tend to rise, positively impacting the Dow.
Investor Sentiment
How to Track the Dow:
You can easily track the Dow through various channels:
Financial News Websites: Many financial news websites, such as CNBC, Bloomberg, and Yahoo Finance, provide real-time updates on the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Investing in the Dow:
There are several ways to invest in the Dow:
Individual Stocks: You can invest directly in the stocks of the 30 companies that make up the Dow.
Important Considerations:
Risk: Investing in the stock market involves inherent risks. The value of stocks can fluctuate significantly, and you could lose money on your investments.
Conclusion
The Dow Jones Industrial Average is a significant benchmark for the U.S. stock market. Understanding the Dow can provide valuable insights into the overall health of the economy and help you make informed investment decisions. By staying informed about the factors that influence the Dow and maintaining a long-term investment perspective, you can navigate the stock market more effectively.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Investing in the stock market involves risks, and you should consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Please note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or investment advice. The Dow Jones Industrial Average is a complex financial instrument, and this article provides a simplified overview.
I hope this article provides a helpful overview of the Dow Jones Industrial Average!


/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25378171/2139238696.jpg?w=200&resize=200,112&ssl=1)


.jpg?auto=webp&format=pjpg&width=3840&quality=60&w=200&resize=200,112&ssl=1)
